fungi life cycle explained
It involves the fusion of the hyphae of two different individuals into a mycelium. Some fungi are single-celled while others are multicellular.
You can think of the spore phase as both the beginning and end of a mushrooms life.
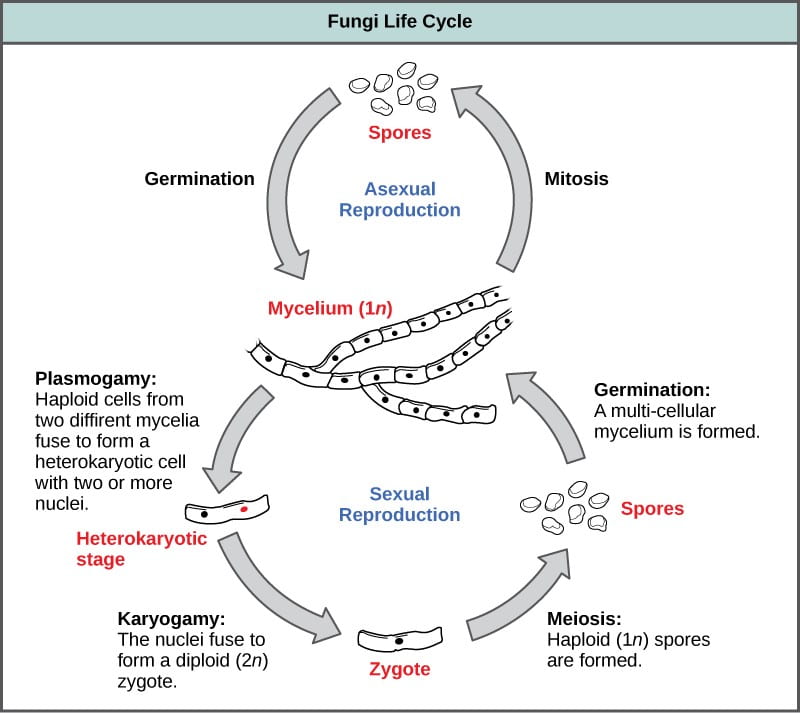
. Spore Haploid The spore phase is the initial stage of the fungal life cycle. Spores produced both. By producing vast numbers of spores both sexually and asexually so in TWO parts of life cycle Major difference from plants.
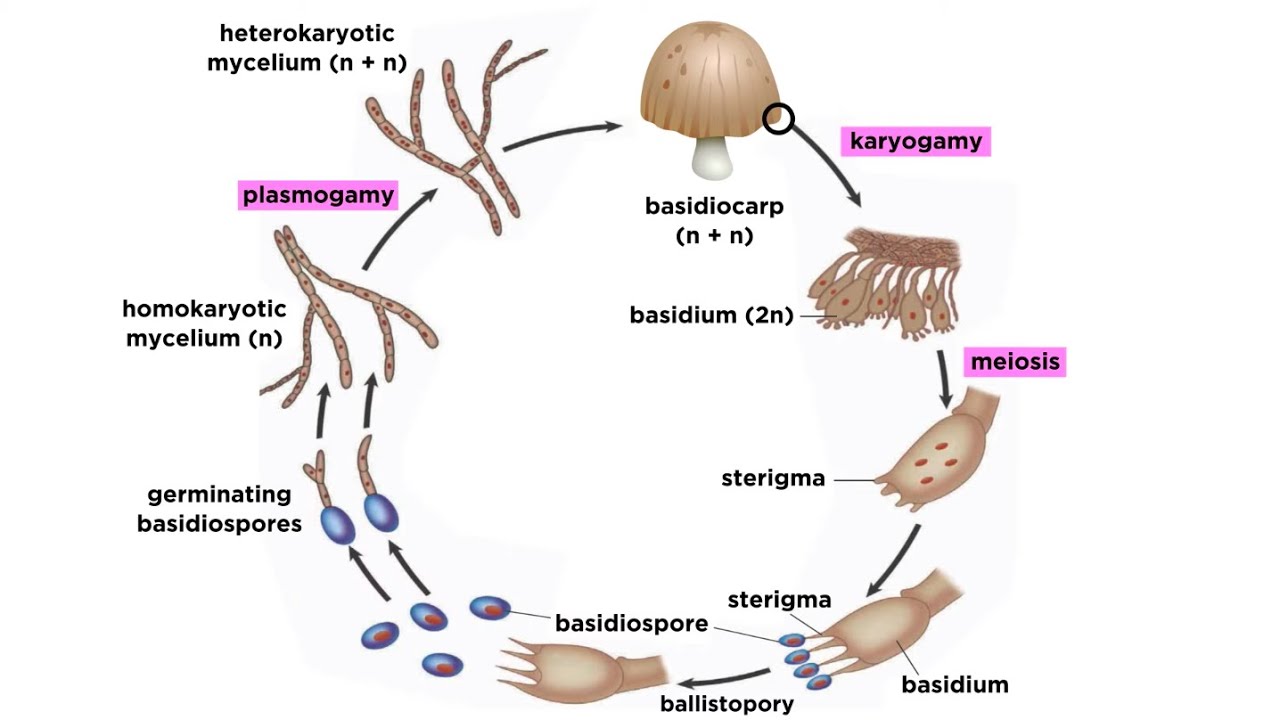
The Basidiomycota basidiomycetes are fungi that have basidia club-shaped structures that produce basidiospores spores produced through budding within fruiting bodies called. Describe the symbiotic relationship of fungi with plants and pathological relationships with other organisms. Being so small and lightweight spores can easily move unseen in the air currents and most fungal spores are spread by the wind.
From these spores haploid hyphae grow and ramify and may give rise to asexual sporangia. Spores are tiny cells that form on special hyphae and are so small that more than 1000 would easily fit on a pinhead. Single-celled fungi are called yeast.
These mushrooms are actually only one part of the organisms life cycle. The life cycle of an ascomycete is characterized by the production of asci during the sexual phase. To form n gametes n.
Great yeast bud scars and pseudohyphae. Fungi can also reproduce by budding and producing spores. This fungus has a dimorphic life cycle with yeast and hyphal stages.
The pseudohyphae can give rise to yeast cells by apical or. The yeast produces hyphae strands and pseudohyphae. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cellsMeiosis reduction division restores the haploid number of chromosomes and initiates.
Macroscopic fungi such as morels mushrooms puffballs and the cultivated agarics available in grocery stores represent only a small fraction of the diversity in the kingdom Fungi. This group of fungi includes almost all mushrooms. All fungi start as haploid spores which means they only have one copy of their genetic information.
This fused cell grows into the fruiting body also known as the mushroom. The haploid phase is the predominant phase of the life cycle. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase.
The life cycle of an ascomycete is characterized by the production of asci during the sexual phase. These fungi are extremely important because they break down decaying matter like wood and plants and allow for their nutrients to return to the soil. Life Cycle Of Receptors G Proteins And Second Messengers Definition Examples Camp Ip3 Pip2 Functions And More Life Cycles Plasma Membrane Cell Biology.
Hyphae are root-like threads composed of haploid cells. The majority of mold. Not all fungi reproduce the same.
This is the first stage in the life cycle of a fungus. This is similar to sperm and eggs which are similar to human sex cells. Life cycle of The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns.
The hyphae are branched septate and uninucleate. In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of phyllactinia with the help of suitable diagrams. Life cycle of fungi.
For most of the molds indoors fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle. The formation of asexual spores is one of the most common ways of asexual reproduction. Despite their diversity in many features the Ascomycetes possess certain common unifying characteristics namely the somatic body composed of a loose indefinite mass of septate mycelium.
The mycelium contains haploid nuclei from both specimens. When two hydra of opposite strain - come into contact the two cell types fuse to create one cell with two nuclei. All fungi begin their life cycle in this stage.
Fungi exist primarily as filamentous dikaryotic organisms. The haploid phase is the predominant phase of the life cycle. Spore germ hypha mature mycelium.
Explain ecosystem services of fungi and human nutrition applications. Sexual Fungi Life Cycle. Sexual reproduction is carried out by diffusion of compatable nuclei from two parent at a definite state in the life cycle of fungi.
As part of their life cycle fungi produce spores. The Basidiomycota basidiomycetes are fungi that have basidia club-shaped structures that produce basidiospores spores produced through budding within fruiting bodies called. In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of ascomycetes explained with the help of a suitable diagram.
These spores migrate far distances through air by grabbing on to other organisms on the way. Mushroom spores are tiny microscopic reproductive units that are produced by fungi as well as some types of plants and algae. But this model provides a good overview in terms of how fungi grows from birth to death.
The process of sexual reproduction involves three phases. Fungi must leave their food to find more and they do this not as hyphae but as spores. Fungus reproduction is not very romantic.
Fungus Life Cycle. Spores produced by mature fungi are released into the surrounding environment where they divide and grow into hyphae. The mycelium is partly internal and partly found on the surface of the host.
The molds for example are a large group of microscopic fungi that include many of the economically important plant parasites allergenic species and opportunistic pathogens of humans and other animals. In this electron micrograph of a mushroom gill the four spores produced by meiosis seen in the center of this picture are carried on a clublike sporangium visible to the left and right. This is where spores come in which are dispersed by wind and can produce a new mycelium.
The fungi life cycle includes both types of reproduction for most species of fungi. Brundrett 1990 showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould. By hitching a ride on another organism or even the wind these spores can travel great.
Fungi life cycle explained Sunday February 27 2022 Edit. A yeast-like fungus commonly occurring on human skin in the upper respiratory alimentary and female genital tracts. The mode of asexrual reproduction.
Sexual reproduction in fungi. The following sections will outline the differences between the. Terms in this set 21 Fungi unique for.
The mycelium spreads on both the surfaces of the host. Home explained full fungi life recruiting wallpaper. In the beginning all spores are haploid which means that they have only a single copy of their entire genetic material.
Fungi cells have a nucleus and organelles like plant and animal cells do. Some fungi alternate between single-celled yeast and multicellular forms depending on what stage of the life cycle they are in. Identify and describe the key adaptations unique to fungi cell walls made of chitin and external digestion including morphological life cycle and metabolic traits.
This leads to the detachment of the bud from the mother cell. The budding involves the formation of a bulge on the side of the cell and the mitotic divide of the nucleus.

How To Draw Rhizopus Labelled Diagram Of Rhizopus Biology Diagrams Draw Diagram Science Diagrams
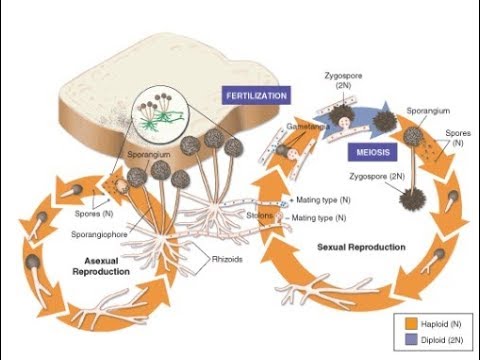
Life Cycle Of Fungus Black Bread Mold Rhizopus Stolonifer Youtube

Life Cycle Of Ferns Fern Life Cycle Biology Plants Plant Science

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fungi Life Cycle In Basidiomycetes Youtube

Reproduction In Fungi Life Cycle Of Fungi Youtube

Generalized Life Cycle Of Fungi Life Cycles Kingdom Fungi Fungi

Basidiomycota Part 2 The Mushroom Life Cycle Youtube

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Life Cycle Of Receptors G Proteins And Second Messengers Definition Examples Camp Ip3 Pip2 Functions And More Life Cycles Plasma Membrane Adenylyl Cyclase
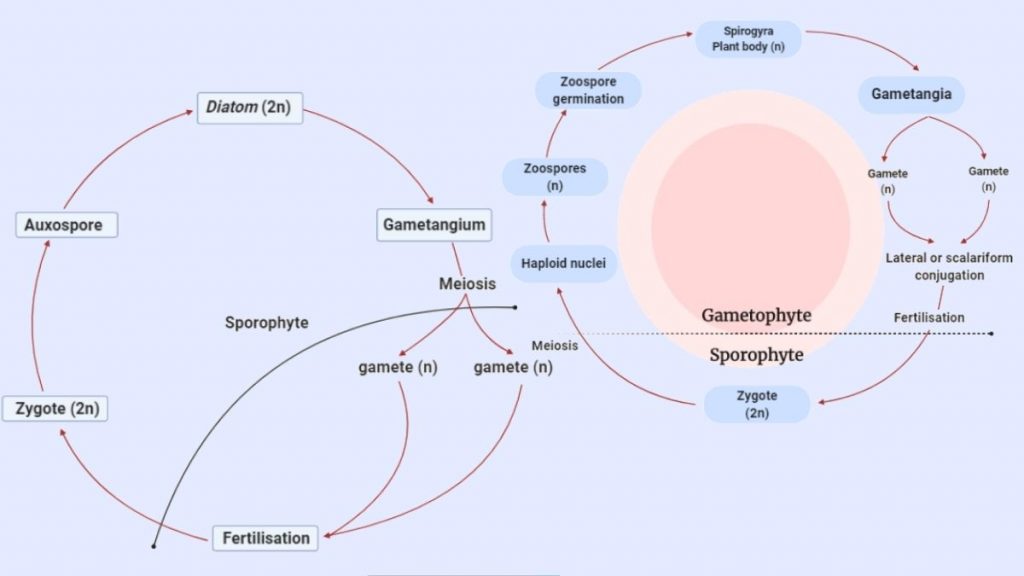
Life Cycle Of Algae Haplontic Diplontic Diplohaplontic And Triphasic

Basidiomycota Life Cycle Study Com

1 Schematic Life Cycle Of The Entomopathogenic Fungi Exemplified By Download Scientific Diagram

Draw Life Cycle Diagrams For Plants Fungi And Animals Study Com

Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids

Life Cycle Of A Fern Genus Polypodium Life Cycles Biology Science Nature